Page 7 - An ultrasound-driven immune-boosting molecular machine for systemic tumor suppression
P. 7
SCIENCE ADVANCES | RESEARCH ARTICLE
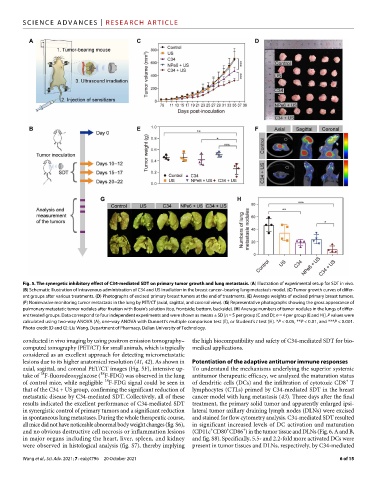
Fig. 5. The synergetic inhibitory effect of C34-mediated SDT on primary tumor growth and lung metastasis. (A) Illustration of experimental setup for SDT in vivo. Downloaded from https://www.science.org at Dalian University of Technology on October 20, 2021
(B) Schematic illustration of intravenous administration of C34 and US irradiation in the breast cancer–bearing lung metastasis model. (C) Tumor growth curves of differ-
ent groups after various treatments. (D) Photographs of excised primary breast tumors at the end of treatments. (E) Average weights of excised primary breast tumors.
(F) Noninvasive monitoring tumor metastasis in the lung by PET/CT (axial, sagittal, and coronal view). (G) Representative photographs showing the gross appearance of
pulmonary metastatic tumor nodules after fixation with Bouin’s solution (top, frontside; bottom, backside). (H) Average numbers of tumor nodules in the lungs of differ-
ent treated groups. Data correspond to four independent experiments and were shown as means ± SD [n = 5 per group (C and D); n = 4 per group (E and H)]. P values were
calculated using two-way ANOVA (A), one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (E), or Student’s t test (H). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
Photo credit (D and G): Liu Wang, Department of Pharmacy, Dalian University of Technology.
conducted in vivo imaging by using positron emission tomography– the high biocompatibility and safety of C34-mediated SDT for bio-
computed tomography (PET/CT) for small animals, which is typically medical applications.
considered as an excellent approach for detecting micrometastatic
lesions due to its higher anatomical resolution (41, 42). As shown in Potentiation of the adaptive antitumor immune responses
axial, sagittal, and coronal PET/CT images (Fig. 5F), intensive up- To understand the mechanisms underlying the superior systemic
18
18
take of F-fluorodeoxyglucose ( F-FDG) was observed in the lung antitumor therapeutic efficacy, we analyzed the maturation status
18
+
of control mice, while negligible F-FDG signal could be seen in of dendritic cells (DCs) and the infiltration of cytotoxic CD8 T
that of the C34 + US group, confirming the significant reduction of lymphocytes (CTLs) primed by C34-mediated SDT in the breast
metastatic disease by C34-mediated SDT. Collectively, all of these cancer model with lung metastasis (43). Three days after the final
results indicated the excellent performance of C34-mediated SDT treatment, the primary solid tumor and apparently enlarged ipsi-
in synergistic control of primary tumors and a significant reduction lateral tumor axillary draining lymph nodes (DLNs) were excised
in spontaneous lung metastases. During the whole therapeutic course, and stained for flow cytometry analysis. C34-mediated SDT resulted
all mice did not have noticeable abnormal body weight changes (fig. S6), in significant increased levels of DC activation and maturation
+
+
+
and no obvious destructive cell necrosis or inflammation lesions (CD11c CD80 CD86 ) in the tumor tissue and DLNs (Fig. 6, A and B,
in major organs including the heart, liver, spleen, and kidney and fig. S8). Specifically, 5.5- and 2.2-fold more activated DCs were
were observed in histological analysis (fig. S7), thereby implying present in tumor tissues and DLNs, respectively, by C34-mediated
Wang et al., Sci. Adv. 2021; 7 : eabj4796 20 October 2021 6 of 15